
CHAPTER 4:
THE COVALENT BOND
Valence Electrons
4-1. Which of the following elements has five valence electrons?
(a) Ca (b) Ga (c) Ge (d) As (e) Se
Answer: (d)
4-2. How many valence electrons are in the IF2- ion?
(a) 7 (b) 14 (c) 20 (d) 21 (e) 22
Answer: (e)
Electronegativity and Bond Polarity
4-3. Which of the following elements is the most electronegative?
(a) S (b) As (c) P (d) Se (e) Cl
Answer: (e)
4-4. Which of the following lists the elements in the correct order of increasing electronegativity?
(a) Si < S < 0 (b) S < Si < 0 (c) S < O < Si (d) Si < O < S (e) O < Si < S
Answer: (a)
4-5. Which series of elements is arranged in order of decreasing electronegativity?
(a) C, Si, P, As, Se (b) O, P, Al, Mg, K (c) Na, Li, B, N, F
(d) K, Mg, Be, O, N (e) Li, Be, B, C, N
Answer: (b)
4-6. Given the following electronegativities: K = 0.8, H = 2.2, and I = 2.5 which of the following statements is true?
(a) H2, I2 and HI are nonpolar covalent compounds.
(b) KI is nonpolar covalent and HI is ionic.
(c) HI is nonpolar covalent and I2 is polar covalent.
(d) H2 is nonpolar covalent, while HI and KI are ionic.
(e) none of the above are true.
Answer: (a)
4-7. In which of the following compounds is the bond the most ionic?
(a) BeF2 (b) CaCl2 (c) SrBr2 (d) BaF2 (e) CaI2
Answer: (d)
4-8. In which of the following compounds is the bond the least polar?
(a) NaCl (b) CH4 (c) CO (d) Cl2 (e) HCl
Answer: (d)
4-9. Which of the following would form compounds with fluorine in which the bond is the least ionic?
(a) P (b) Ca (c) Al (d) O (e) Se
Answer: (d)
4-10. Which of the following compounds is most likely to be on the borderline between ionic and covalent compounds?
(a) MgO (b) MgBr2 (c) Al2O3 (d) AlF3 (e) AlBr3
Answer: (e)
Lewis Structure
4-11. Which of the following atoms, ions or molecules could combine to form a stable covalent bond?
(a) CH4 and H- (b) BF3 and F- (c) H and F- (d) Ar and BF3 (e) Ar and CH4
Answer: (b)
4-12. The correct Lewis structure for CH2Cl2 contains:
(a) 2 single bonds, 2 double bonds and no nonbonding electrons
(b) 4 single bonds and no nonbonding electrons
(c) 4 single bonds and four nonbonding electrons
(d) 2 single bonds, 2 double bonds, and eight nonbonding electrons
(e) 4 single bonds and 12 nonbonding electrons.
Answer: (e)
4-13. The correct Lewis structure for the NO2+ ion has:
(a) 2 double bonds and eight nonbonding electrons
(b) 1 double bond, 1 single bond, and 12 nonbonding electrons
(c) 2 single bonds and 12 nonbonding electrons
(d) 2 triple bonds and 4 nonbonding electrons
(e) 1 single bond, 1 double bond, and 8 nonbonding electrons
Answer: (a)
4-14. Which of the following are exceptions to the Lewis octet rule?
(I) CO2 (II) BeF2 (III) SF4 (IV) SO3 (V) PCl3
(a) I and II (b) II and III (c) III and IV
(d) I, II and III (e) none of these are exceptions to the Lewis octet rule
Answer: (b)
4-15. Which of the following are exceptions to the Lewis octet rule?
(I) BF3 (II) H2CO (III) XeF4 (IV) H3O+ (V) ClF3
(a) I and II (b) I and III (c) I, III and V
(d) II and III (e) III and V
Answer: (c)
4-16. Which of the following compounds contains only single bonds?
(a) CN- (b) NO+ (c) CO (d) O22- (e) Cl2CO
Answer: (d)
4-17. Which of the following would be the best Lewis structure for NOCl?

Answer: (c)
4-18. Which of the following compounds would have the same electron configuration as the N2 molecule?
(I) CaO (II) CO (III) NO (IV) CN- (V) NO+
(a) I (b) II and IV (c) II and III (d) II, IV and V (e) IV and V
Answer: (d)
4-19. Which of the following would have a Lewis structure most like that of CO32- ion?
(a) CH3+ (b) NH3 (c) NO3- (d) SO32- (e) SO42-
Answer: (c)
4-20. Which of following molecules is best described with two resonance structures?
(a) NO2- (b) H2O (c) OF2 (d) ClNO (e) BeF2
Answer: (a)
4-21. Which of the following isn’t a resonance hybrid?
(a) CO2 (b) NO2- (c) N2O (d) SO3 (e) SCN-
Answer: (a)
4-22. Which of the following are resonance hybrids?
(I) HCO2- (II) PH3 (III) HCN (IV) SO42- (V) NO2
(a) I (b) II and IV (c) IV and V
(d) I and IV (e) I and V
Answer: (e)
4-23. Which of the following compounds contains the strongest carbon-nitrogen bond? (Hint: Look at their Lewis structures)
(a) H2CNH (b) HCN (c) H3CNH2 (d) H3CNO
(e) all of these molecules contain C-N single bonds.
Answer: (b)
4-24. Which of the following elements would form a compound with the following Lewis structure?
![]()
(a) Be (b) B (c) C (d) N (e) O (f) F
Answer: (d)
4-25. If there are two pairs of nonbonding electrons in the valence shell of the central atom in the XF4- ion, in which Group of the periodic table does the element X belong?
(a) Group IVA (b) Group VA (c) Group VIA
(d) Group VIIA (e) Group VIIIA
Answer: (d)
4-26. What is element X in the following Lewis structure?
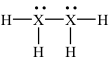
(a) B (b) C (c) N (d) O (e) F
Answer: (c)
4-27. Which element will combine with sulfur to form a linear molecule with the formula XS2? (a) Li (b) Be (c) C (d) O (e) F
Answer: (c)
4-28. Which element would form an XF62- ion for which there are no nonbonding electrons in the Lewis structure?
(a) N (b) Al (c) Si (d) P (e) Br
Answer: (c)
4-29. If X is a 3rd row element and XO2 has the Lewis structure
![]()
X must be:
(a) Al (b) Si (c) P (d) S (e) Cl
Answer: (d)
4-30. If the XF6- ion has the Lewis structure
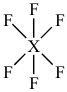
X could be which of the following elements?
(a) N (b) Al (c) Si (d) P (e) Br
Answer: (d)
4-31. Assume that the XF3 molecules has the following Lewis structure.
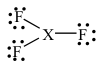
The molecule could be:
(a) boron trifluoride, i.e., X = B
(b) nitrogen trifluoride, i.e., X = N
(c) chlorine trifluoride, i.e., X = Cl
(d) phosphorus trifluoride, i.e., X = P
(e) more than one of the above
Answer: (a)
4-32. Nitrous oxide (N2O) is an anesthetic commonly known as “laughing gas.” In spite of the brilliant performance by Steve Martin in the movie “The Little Shop of Horrors,” it doesn’t always induce laughing. Sometimes people get hysterical. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for this compound?

Answer: (c)
Formal Charge
4-33. In lecture, we analyzed the formal charge on the so-called “zwitterion” form of the amino acid glycine: H3N+CH2CO2-. The properties of the various amino acids depend heavily on the presence (or absence) of charge on the side chain. Consider the amino acid arginine, for example, which has the following Lewis structure:

Once again, there is a positive charge on the amine on the amino acid backbone, which we can ignore. What about the nitrogens labeled 1, 2 and 3 on the side chain? Are they neutral, negatively charged, or positively charged?
(a) N(1) = 0, N(2) = +1, and N(3) = 0
(b) N(1) = 0, N(2) = -1, and N(3) = 0
(c) N(1) = +1, N(2) = 0, and N(3) = +1
(d) N(1) = -1, N(2) = 0, and N(3) = -1
(e) N(1) = +1, N(2) = 0, and N(3) = -1
4-34. The American response to the attack on World Trade Center involved using 40-year old B-52's to drop cluster bombs on Afghanistan. Our response to the anthrax scare was a 20-year old antibacterial known as ciprofloxacin or “Cipro.”
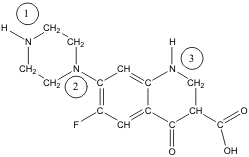
Apply the concept of formal charge to the three nitrogen atoms labeled 1, 2 and 3 on the side chain? Are they neutral, negatively charged, or positively charged?
(a) N(1) = -1, N(2) = -1, and N(3) = -1
(b) N(1) = -1, N(2) = 0, and N(3) = 0
(c) N(1) = 0, N(2) = 0, and N(3) = 0
(d) N(1) = 0, N(2) = +1, and N(3) = +1
(e) N(1) = +1, N(2) = +1, and N(3) = +1
Bonding and Nonbonding Pairs
4-35. How many pairs of bonding electrons are in the valence shell of the iodine atom in the IF2- ion?
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4
Answer: (c)
4-36. How many pairs of nonbonding electrons are in the valence shell of the iodine atom in the IF2- ion?
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4
Answer: (d)
4-37. How many pairs of nonbonding electrons are in the valence shell of the iodine atom in the ICl4- ion?
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4
Answer: (c)
4-38. How many nonbonding electrons are on the central atom in the Lewis structure of xenon tetrafluoride?
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4
Answer: (e)
4-39. How many pairs of bonding electrons can be found in the valence shell of the nitrogen atom in HNO2? (Hint: the skeleton structure is HONO)
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4
Answer: (d)
4-40. How many pairs of nonbonding electrons can be found on the chlorine atom in chlorous acid, HOClO?
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4
Answer: (c)
4-41. Which of the following elements would form an XF62- ion that has no nonbonding electrons in the valence shell of the central atom?
(a) Ca (b) C (c) Si (d) S (e) P
Answer: (c)
4-42. Which of the following species has all its electrons paired?
(a) Fe3+ (b) Zn2+ (c) ClO2 (d) NO (e) NO2
Answer: (b)
Molecular Geometry
4-43. In which compound are the valence electrons on the sulfur arranged towards the corners of a tetrahedron?
(a) SF3+ (b) SF4 (c) SF5 (d) SF6 (e) both SF4 and SF6
Answer: (a)
4-44. What is the distribution of electrons around the S atom in H2SO4? [Hint: The skeleton structure of this oxyacid is O2S(OH)2.]
(a) linear (b) trigonal planar (c) tetrahedral
(d) trigonal bipyramidal (e) octahedral
Answer: (c)
4-45. What is the distribution of electrons around the N atom in HNO3? (Hint: The skeleton structure of this oxyacid is HONO2)
(a) linear (b) trigonal planar (c) tetrahedral
(d) trigonal bipyramidal (e) octahedral
Answer: (b)
4-46. There is a single pair of nonbonding electrons on the central atom in the Lewis structure of ICl5. This molecule has:
(a) A trigonal pyramidal distribution of electrons and an octahedral molecular geometry
(b) An octahedral distribution of electrons and a square pyramidal geometry
(c) A trigonal bipyramidal distribution of electrons and a see-saw molecular geometry
(d) An octahedral distribution of electrons and a trigonal bipyramidal geometry
(e) A trigonal bipyramidal distribution of electrons and trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
Answer: (b)
4-47. The bond angles in most symmetric, ABx, molecules are the same. Which of the following is an exception to this rule?
(a) NH3 (b) SF6 (c) PCl5 (d) SO3 (e) CO2
Answer: (c)
4-48. Which term best describes the shape of the I3- ion?
(a) linear (b) bent (c) trigonal planar
(d) trigonal pyramidal (e) trigonal bipyramidal
Answer: (a)
4-49. What is the molecular geometry of the compound formed by the reaction of nitrogen with fluorine?
(a) bent (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal pyramidal
(d) trigonal bipyramidal (e) none of the above
Answer: (c)
4-50. What is the molecular geometry of the SF5+ ion?
(a) see-saw (b) square planar (c) square pyramidal
(d) trigonal bipyramidal (e) octahedral
Answer: (d)
4-51. What is the molecular geometry of xenon tetrafluoride?
(a) tetrahedral (b) trigonal bipyramidal (c) see-saw
(d) square planar (e) octahedral
Answer: (d)
4-52. The shape of the NO2- ion is best described as:
(a) linear (b) T-shaped (c) bent
(d) square planar (e) pyramidal
Answer: (c)
4-53. What is the best description of the structure of the SF3+ ion?
(a) bent or angular (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal pyramidal
(d) tetrahedral (e) trigonal bipyramidal
Answer: (c)
4-54. The molecular structure of the IO3- ion is best described as:
(a) bent or angular (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal pyramidal
(d) trigonal bipyramidal (e) T-shaped
Answer: (c)
4-55. Which of the following molecules is a Lewis acid that has a trigonal planar shape?
(a) BeCl2 (b) PCl3 (c) Ca(OH)2 (d) BF3 (e) H3O+
Answer: (d)
4-56. Which of the following molecules are best described as bent or angular in shape?
(I) H2S (II) CO2 (III) ClNO (IV) NH2- (V) O3
(a) I and II (b) I, III and IV (c) I, III, IV and V
(d) II, III and IV (e) All of these molecules are bent or angular in shape
Answer: (c)
4-57. Which of the following molecules are planar?
(I) SO3 (II) SO32- (III) NO3- (IV) PF3 (V) BH3
(a) I and II (b) I and III (c) I, III and V (d) II and IV (e) III and V
Answer: (c)
4-58. Which of the following molecules are tetrahedral?
(I) SiF4 (II) CH4 (III) NF4+ (IV) BF4- (V) TeF4
(a) I and II (b) I, II and III (c) I, II, III and IV
(d) II, III and IV (e) V
Answer: (c)
4-59. Which of the following molecules are linear?
(I) C2H2 (II) CO2 (III) NO2- (IV) NO2+ (V) H2O
(a) I and II (b) I, II and III (c) I, II and IV
(d) II and III (e) V
Answer: (c)
4-60. Which of the following has a square-planar shape?
(a) SF4 (b) ClO4- (c) CCl4 (d) ICl4- (e) PO43-
Answer: (d)
4-61. Which of the following compounds have the same shape or geometry?
(a) NH2- and H2O (b) NH2- and BeH2
(c) H2O and BeH2 (d) NH2-, H2O and BeH2
Answer: (a)
4-62. Which of the following compounds have the same shape or geometry?
(a) SF4 and CH4 (b) CO2 and H2O (c) CO2 and BeH2
(d) N2O and NO2 (e) PCl4+ and PCl4-
Answer: (c)
4-63. Which of the following molecules or ions doesn’t have a tetrahedral shape?
(a) SiF4 (b) NF4+ (c) BF4- (d) SeF4 (e) CF4
Answer: (d)
4-64. Which of the following molecules or ions isn’t planar?
(a) NH3 (b) BF3 (c) CO32- (d) NO3-
(e) all of these molecules or ions are planar.
Answer: (a)
4-65. Which of the following species isn’t planar?
(a) SO3 (b) SO32- (c) SO2 (d) BF3 (e) NO3-
Answer: (b)
4-66. According to the VSED theory, the distribution of electrons in the valence shell of the central atom of a molecule can be predicted from the Lewis structure of that molecule. What is the distribution of electrons in the valence shell of the Xe atom in the XeF3+ ion? (a) trigonal planar (b) tetrahedral (c) square planar
(d) trigonal bipyramidal (e) octahedral
Answer: (d)
4-67. What would be the best description of the shape of the XeF3+ ion?
(a) linear (b) bent (c) see-saw (d) T-shape (e) tetrahedral
Answer: (d)
4-68. Tellurium hydride is one of the foulest smelling compounds known. How many pairs of nonbonding electrons are in the valence shell of the tellurium atom in TeH2?
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4
Answer: (c)
4-69. What is the best description of the distribution of electrons in the valence shell of the tellurium atom in TeH2?
(a) linear (b) trigonal planar (c) tetrahedral
(d) trigonal bipyramidal (e) octahedral
Answer: (c)
4-70. What is the best description of the shape of the TeH2 molecules?
(a) linear (b) bent (c) trigonal planar (d) tetrahedral (e) see-saw
Answer: (b)
4-71. The best way for the body to get rid of excess nitrogen from the metabolism of proteins is by excreting urea, a planar molecule which has the following Lewis structure.
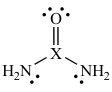
Which element does the "X" stand for in this Lewis structure?
(a) C (b) N (c) O (d) P (e) S
Answer: (a)
4-72. If there is a single pair of nonbonding electrons on the "X" atom in the Lewis structure of XF4, in which group of the periodic table would you be the most likely to find element "X"?
(a) Group IlIA (b) Group IVA (c) Group VA (d) Group VIA (e) Group VIIA
Answer: (d)
4-73. What would be the distribution of electrons in the valence shell of the "X" atom in the previous question?
(a) trigonal planar (b) tetrahedral (c) trigonal bipyramidal
(d) octahedral (e) none of these
Answer: (c)
4-74. What would be the shape of the XF4 molecule in the previous questions?
(a) octahedral (b) see-saw (c) tetrahedral
(d) square pyramidal (e) trigonal bipyramidal
Answer: (b)
4-75. Which element would form a neutral XF3 molecule with a trigonal planar geometry?
(a) Be (b) B (c) C (d) N (e) Cl
Answer: (b)
4-76. The compound XCl3 has a trigonal pyramidal geometry. Element Z is a member of:
(a) Group IIA (b) Group IlIA (c) Group VA (d) Group VIA (e) Group VIIA
Answer: (c)
4-77. Last year, Stan Freeburg noted three names that occupied so much of the news in recent years – Monica Lewinsky (the White House aid), Tara Lipinski (The Olympic Champion), and Theodore Kaczynski (the Unabomber) – all rhyme. Obviously a conspiracy! During the peak years of the witch-hunt for communist conspiracies, Marie Curie’s daughter – Irene Curie Joliot – was turned down for membership in the American Chemical Society solely because she was a communist. This led Linus Pauling, one of the foremost chemists of the 20th century, to resign from the ACS. Pauling won two Nobel Prizes, one for chemistry and one for peace. One of his many contributions was the theory of hybridization, with which he explained the observed shapes of molecules. Which of the following set of hybrid orbitals would give rise to an trigonal bipyramidal geometry?
(a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) sp3d (e) sp3d2
Answer: (d)
4-78. An element we will represent as X forms a compound with the empirical formula XCl5 that undergoes an interesting reaction when it crystallizes to form a mixed salt of XCl4+ and XCl6- ions. Assume that XCl4+ has a tetrahedral geometry and there are no nonbonding electrons in the valence shell of the X atom. In which column of the periodic table are you most likely to find element X?
(a) Group IVA (C, Se, Ge ...) (b) Group VA (N, P, As ...)
(c) Group VIA (O, S, Se ... (d) Group VIIA (F, Cl, Br ...)
(e) Group VIIIA (He, Ne, Ar, ...)
Answer: (b)
4-79. Metformin is the chemical name for a prescription drug sold as “glucophage,” which is an oral hypoglycemic. In other words, a pill that lowers blood sugar levels, so that adult on-set diabetics don’t have to inject themselves with insulin. The Lewis structure of metformin is shown below.
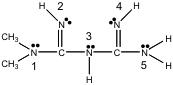
Use the VSEPR or VSED theories to predict the geometry around the nitrogen atom in the center of the molecule, e.g., N(3).
(a) bent or angular (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal pyramidal
(d) trigonal bipyramidal (e) tetrahedral
Answer: (c)
4-80. Terpin hydrate is an expectorant that was used for many years by people with serious coughs, such as those suffering from pneumonia.
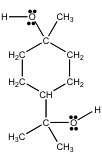
Use the VSEPR theory to predict the distribution of electrons in the valence shell of the oxygen atoms in this compound.
(a) linear (b) bent or angular (c) trigonal planar (d) tetrahedral
(e) trigonal bipyramidal
Answer: (d)
4-81. When the rare gas elements (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe and Rn) were first discovered, a sample of Ar was sent to Moissan, who had discovered the most active of the known elements: F2. The failure of Moissan's attempts to react argon with fluorine, coupled with repeated failures by other chemists to get the more abundant of these gases to undergo chemical reaction, eventually led to their being labeled inert gases. We now know this isn’t so. Xe reacts with F2 to form a variety of compounds, including XeF4. Which of the following best describes the XeF4 molecule?
(a) Trigonal bipyramidal distribution of valence electrons on the Xe with a T-shaped molecular geometry.
(b) Trigonal bipyramidal distribution of valence electrons on the Xe with a trigonal planar molecular geometry.
(c) Trigonal bipyramidal distribution of valence electrons on the Xe with a pyramidal molecular geometry.
(d) Octahedral distribution of valence electrons on the Xe with a square planar molecular geometry.
(e) Octahedral distribution of valence electrons on the Xe with a see-saw molecular geometry.
Answer: (d)
4-82. At a seminar on “everything you want to know about research at Unilever” a chemist talked about how they used the blue complex that forms when the I3- ion is added to starch to stain dishes to test their new — and improved! — liquid detergent. How many pairs of nonbonding electrons are in the valence shell of the central iodine atom in the I3- ion?
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4
Answer: (d)
4-83. The Raschig process involves the reaction between ammonia and the hypochlorite ion to form hydrazine, which has been used as a rocket fuel.
2 NH3(aq) + OCl-(aq) ➝ H2NNH2(g)
There are isolated cases of individuals making hydrazine unexpectedly in their homes when cleaning a commode. They start with a cleaner that contains ammonia, and then, when this doesn’t work, they mix it with a cleaner (such as Chlorox) that contains the hypochlorite ion. How many pairs of nonbonding electrons can be found on each nitrogen atom in the hydrazine molecule? (Note: Assume that there is a bond between the two nitrogen atoms in hydrazine.)
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3
(e) The two N atoms contain a different number of nonbonding electrons.
Answer: (b)
4-84. Predict the distribution of electrons in the valence shell of the nitrogen atoms in hydrazine.
(a) linear (b) bent or angular (c) trigonal planar
(d) trigonal pyramidal (e) tetrahedral
Answer: (e)
4-85. Use the VSEPR theory to predict the geometry around each nitrogen atom in hydrazine.
(a) linear (b) bent or angular (c) trigonal planar
(d) trigonal pyramidal (e) tetrahedral
Answer: (d)
Hybridization
4-86. Which type of hybrid orbitals are used by the carbon atom in CO2?
(a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) dsp3 (e) d2sp3
Answer: (a)
4-87. In which of the following compounds is the central nitrogen atom sp2 hybridized?
(a) NO2+ (b) NO2 (c) NO2- (d) NO3- (e) NO2, NO2- and NO3-
Answer: (e)
4-88. What is the hybridization of the nitrogen atom in the N2 molecule?
(a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) sp3d (e) sp3d2
Answer: (a)
4-89. What is the hybridization of central iodine atom in the I3- ion?
(a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) sp3d (e) sp3d2
Answer: (d)
4-90. What is the hybridization of the sulfur atom in the SF3+ ion?
(a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) sp3d (e) sp3d2
Answer: (c)
4-91. What is the hybridization of the beryllium atom in BeF2?
(a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) sp3d (e) sp3d2
Answer: (a)
4-92. What is the hybridization of the xenon atom in the XeF3+ ion?
(a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) sp3d (e) sp3d2
Answer: (d)
4-93. What is the hybridization of the nitrogen atom in the NO2+ ion?
(a) sp (b) sp2 (c) sp3 (d) sp3d (e) sp3d2
Answer: (a)
4-94. The central atom in all of the following compounds has the same hybridization, except: (a) NO2- (b) CO32- (c) BF3 (d) NH3
(e) the hybridization is the same in all of these compounds
Answer: (d)
Molecular Orbital Theory
4-95. As noted in last year’s exam, the drug for which more prescriptions – and more bad jokes – were written recently has the scientific name Sildenafil citrate and the trade name Viagra™. Viagra™ works by inducing the release of nitrogen oxide (NO) from endothelial cells, which diffuses into the smooth muscles where it binds to an enzyme called guanylate cyclase, which induces the synthesis of cyclic GMP, which induces the muscle cells to release Ca2+ ions, which allows the muscle cells to relax, which allows blood to flow, and so on. Use the following molecular orbital diagram to predict which of the following has the largest bond order:

(a) NO+ (b) NO (c) NO- (d) all of the above have the same bond order
Answer: (a)
4-96. Use the same molecular orbital diagram to predict which of the following molecules should be paramagnetic.
(I) B2 (II) C2 (III) N2 (IV) O2 (V) F2
(a) I (b) I and II (c) I and IV (d) I, II and IV (e) II, III and IV
Answer: (c)