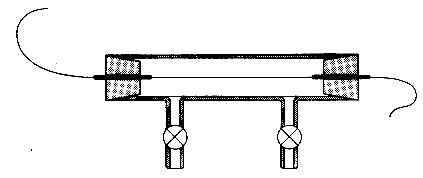
An iron wire is enclosed in a glass vessel (variac) and is purged with N2 or Ar to prevent a reaction with O2.
Chemical Concepts Demonstrated: The effect of temperature on the structure of a solid; body-centered and face-centered cubic
Demonstration:

An iron wire is enclosed in a glass vessel (variac) and is purged with
N2 or Ar to prevent a reaction with O2.
A voltage of 6-8 volts is sent through the wire.
Observations:
When the temperature of the wire exceeds 910 °C, the wire sags. When
the variac is off, the wire returns to its inital dimensions.
Explanation:
Iron crystallizes in a body centered cubic structure at room temperature. The density of iron in this phase (7.86 g/cm3) implies an atomic radius of 0.124 nm. At around 910 °C, pure iron changes from body-centered cubic to face-centered cubic packing. This phase change results is accompanied by a decrease in the density of the iron, and the iron wire sags. From this decrease in density, it is assumed that the atomic radius of the iron atom at 910 °C must be significantly larger than at room temperature.