- The crystallizing dishes are half-filled with the filtrate.
- AgNO3 is added to the first dish.
- NaOAc is added to the second.
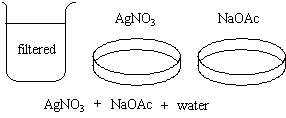
Chemical Concept Demonstrated: Common-ion effect
Demonstration:
AgNO3 and NaOAc are added to a beaker of water, and the solution is
filtered.
|
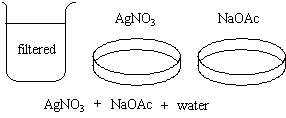 |
Observations:
AgOAc precipitates in both dishes.
Explanation (including important chemical equations):
The common-ion effect is the decrease in the solubility of a salt that occurs when the salt is dissolved in a solution that contains another source of one of its ions. The filtrate is a saturated solution of Ag+ and OAc- ions. When either AgNO3 or NaOAc is added to the filtrate, the solubility of the ions in the saturated solution decreases, and the Ag + and OAc- ions crash out as AgOAc.
AgNO3 (aq) + OAc - (aq) <=> AgOAc (s)
NaOAc (aq) + Ag + (aq) <=> AgOAc (s)