A copper wire electrode along with a magnesium electrode are inserted into the solution.
The wires are connected to a flashbulb.
Alternately, a normal light bulb may be used.
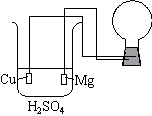
Chemical Concept Demonstrated: Electrochemical work with voltaic or galvanic cells
Demonstration:
| The beaker contains a solution of H2SO4. A copper wire electrode along with a magnesium electrode are inserted into the solution. The wires are connected to a flashbulb. Alternately, a normal light bulb may be used. |
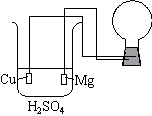 |
Observations:
The flashbulb is set off.
Explanation (including important chemical equations):
The standard-state reduction potentials are:
| Mg 2+ (aq) + 2 e- ---> Mg (s) | Eo = -2.37 V |
| Cu 2+ (aq) + 2 e- ---> Cu (s) | Eo = 0.34 V |
The reaction that has an overall positive cell potential is therefore
| Mg (s) ---> Mg 2+ (aq) + 2 e- | Eo = 2.37 V |
| 2 H + (aq) + 2 e - ---> H2 (g) | Eo = 0.00 V |
| Mg (s) + 2 H + (aq) ---> Mg 2+ (aq) + H2 (g) | Eo cell = 2.37 V |
Electrons flow from the magnesium electrode to the copper electrode through the external circuit, setting off the flashbulb.