22.16 Formaldehyde Clock Reaction-- Red/Green Race
Chemical Concepts Demonstrated: Concentration
effects on reaction rate, addition reactions across a C=O double bond
Demonstration:
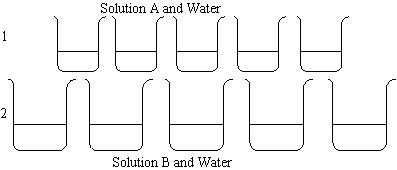
The first set of beakers contains varying amounts of solution A and water. The second
set of beakers contains varying amounts of solution B and water. One set has green
indicator, the other red.
- Solution A: Formalin (37% formaldehyde) diluted.
- Solution B: NaHSO3, Na2SO3, and
disodium EDTA dissolved in water and diluted.
- Green Indicator: Thymolphthalein mixed with p-nitrophenol
solution.
- Red Indicator: Phenolphthalein mixed with p-nitrophenol
solution.
|
 |
Observations:
The clock reaction shown proceeds in a linear fasion. The
beakers on the left change first while the beakers on the right change last.
Explanation:
The beakers change color at different rates because of the different
concentrations of starting materials, particularly the materials involved in the
rate-limiting step, the production of formaldehyde:
CH2(OH)2 --> HCHO + H2O
The faster the formaldehyde is produced, the faster the beakers
change color.
