Practice Problem 8
Methyllithium (CH3Li) can be used to form bonds between carbon and either main-group metals or transition metals:
HgCl2(s) + 2 CH3Li(l) ![]() Hg(CH3)2(l)
+ 2 LiCl(s)
Hg(CH3)2(l)
+ 2 LiCl(s)
WCl6(s) + 6 CH3Li(l) ![]() W(CH3)6(l)
+ 6 LiCl(s)
W(CH3)6(l)
+ 6 LiCl(s)
It can be used also to form bonds between carbon and other nonmetals:
PCl3(s) + 3 CH3Li(l) ![]() P(CH3)3(l)
+ 3 LiCl(s)
P(CH3)3(l)
+ 3 LiCl(s)
or between carbon atoms:
CH3Li(l) + H2CO(g) ![]() [CH3CH2OLi]
[CH3CH2OLi]
![]() CH3CH2OH(l)
CH3CH2OH(l)
Use Lewis structures to explain the stoichiometry of the following oxidation-reaction, which is used to synthesize methyllithium:
CH3Br(l) + 2 Li(s) ![]() CH3Li(l)
+ LiBr(s)
CH3Li(l)
+ LiBr(s)
Answer
The active metals are reducing agents in all of their chemical reactions. In this reaction, lithium metal reduces a carbon atom from an oxidation state of -2 to -4, as shown below:
Reduction: CH3Br + 2 e- ![]() CH3Li
CH3Li
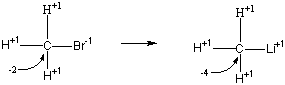
The other half of the reaction therefore must involve the net loss of a total of two electrons:
Oxidation: 2 Li ![]() 2 Li+ + 2 e-
2 Li+ + 2 e-
Two moles of lithium are therefore consumed for each mole of CH3Br in this reaction. One of the Li+ ions formed in this reaction combines with the negatively charged carbon atom to form methyllithium and the other participates from solution with the Br - ion as LiBr:
CH3Br(l) + 2 Li(s) ![]() CH3Li(l)
+ LiBr(s)
CH3Li(l)
+ LiBr(s)