Zn(s) + 2 H+(aq)
![]() Zn2+(aq) + H2(g)
Zn2+(aq) + H2(g)
Practice Problem 10
Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25oC for the reaction between zinc metal and acid.
Zn(s) + 2 H+(aq)
Zn2+(aq) + H2(g)
Solution
We start by calculating the overall standard-state cell potential for this reaction.
| Zn |
Eoox = -(-0.7628 V) | ||
| + 2 H+ + |
Eored = 0.0000 V | ||
| ŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻ | ŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻŻ | ||
| Zn(s) + 2 H+(aq)
|
Eo = 0.7628 V |
We then substitute into the Nernst equation the implications of the fact that the reaction is at equilibrium: Qc = Kc and E = 0.
![]()
We then rearrange this equation
![]()
and solve for the natural logarithm of the equilibrium constant.
![]()
Substituting what we know about the reaction into this equation gives the following result.
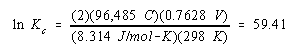
![]()
This is a very large equilibrium constant, which means that equilibrium lies heavily on the side of the products. The equilibrium constant is so large that the equation for this reaction is written as if it proceeds to completion.
Zn(s) + 2 H+(aq)
![]() Zn2+(aq)
+ H2(g)
Zn2+(aq)
+ H2(g)